

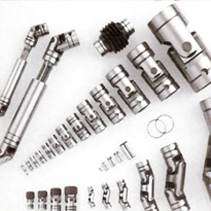








Gear couplings are mechanical devices used to transmit torque between two rotating shafts. They consist of two hubs with external teeth, and a sleeve with internal teeth that fits over the hubs. The teeth on the hubs and sleeve mesh together, creating a strong and precise connection between the two shafts.
One of the primary advantages of gear couplings is their ability to handle high torque and misalignment. They are capable of transmitting torque over long distances and can compensate for both angular and parallel misalignment between the shafts. This makes them ideal for use in heavy-duty machinery such as turbines, compressors, and pumps.
Gear couplings also offer excellent reliability and durability. The teeth on the hubs and sleeve are designed to withstand high stress and wear, and they require minimal maintenance. Additionally, gear couplings are resistant to shock and vibration, which helps to reduce the risk of damage to the machinery.
There are several different types of gear couplings available, each with its own specific features and benefits. For example, some gear couplings have a torsionally flexible design that helps to reduce the effects of shock loads and vibration. Others have a compact and lightweight design that makes them ideal for use in tight spaces.
In conclusion, gear couplings are an important component in many types of machinery. They offer high torque capacity, excellent reliability, and durability, and are capable of compensating for misalignment. Whether you are designing a new piece of equipment or maintaining an existing one, gear couplings are an excellent choice for transmitting torque between rotating shafts.

















